Steelmaking is the process of getting the pig iron into a steelmaking furnace and melting it according to a certain process. According to the survey online, steel products include steel ingots, continuous casting billets, and direct casting into various steel castings. Generally speaking, steel generally refers to steel that is rolled into various steel materials. Steel is a ferrous metal but steel is not exactly equal to ferrous.
Introduce the Specific Process and Steps of Steelmaking
Slag Formation: The operation of adjusting the slag composition, alkalinity, and viscosity and its reaction ability in steel and iron production. The purpose is to produce a metal having the desired composition and temperature by a slag-metal reaction. For example, oxygen top-blown converter slagging and oxygen blowing operations are to produce slag with sufficient fluidity and alkalinity, which can transfer enough oxygen to the molten metal surface to reduce sulfur and phosphorus below the upper limit of the planned steel grade. The amount of splashing and spilling during oxygen blowing is minimized.
Slag Discharge: slagging or slag operation taken during smelting according to different smelting conditions and purposes during electric arc furnace steelmaking. When smelting with the single slag method, the oxidized slag must be slag at the end of the oxidation; when the slag is reduced by the double slag method, the original oxidized slag must be completely released to prevent phosphorus from being returned.
Molten Pool Stirring: Supplying energy to the molten metal pool to cause movement of the molten metal and slag to improve the kinetic conditions of the metallurgical reaction. The molten pool agitation can be achieved by means of gas, mechanical, electromagnetic induction and the like.
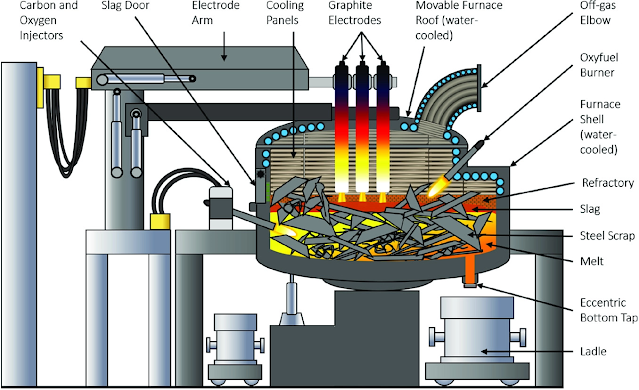
The Bottom Blowing of the Electric Arc Furnace: N2, Ar, CO2, CO, CH4, O2, and other gases are blown into the molten pool of the furnace according to the process requirements by nozzles placed at the bottom of the furnace to accelerate the melting and promote the metallurgical reaction process. The bottom blowing process can shorten the smelting time, reduce the power consumption, improve the dephosphorization and desulfurization operations, increase the amount of residual manganese in the steel, and increase the yield of metals and alloys. It can make the molten steel composition and temperature more uniform, thus improving steel quality, reducing cost and increasing productivity.
Melting Period: The melting period of steelmaking is mainly for open-hearth and electric arc furnace steelmaking. The electric arc furnace steelmaking is called the melting period from the start of the energization until the charge is completely melted, and the open hearth steelmaking is completed from the completion of the molten iron to the completion of the charge. The task of the melting period is to melt and heat the charge as soon as possible, and to make the slag in the melting period.
Oxidation Period and Decarbonization Period: The oxidation period of ordinary power arc furnace steelmaking usually refers to the process stage of melting, sampling, and analysis of the furnace to the completion of oxidation. It is also believed to start with oxygen blowing or decarburization. The main task of the oxidation period is to oxidize carbon and phosphorus in the molten steel; remove gases and inclusions; and uniformly heat the molten steel. Decarburization is an important process in the oxidation phase. In order to ensure the purity of the steel, the amount of decarburization is required to be greater than about 0.2%. With the development of refining technology outside the furnace, most of the oxidative refining of the electric arc furnace is moved to a ladle or a refining furnace.
Refining Period: The steelmaking process through the slagging and other methods to remove some of the elements and compounds that are harmful to the quality of the steel, chemically selected into the gas phase or discharged into the slag to remove it from the molten steel process.
Reduction Period: In the ordinary power arc furnace steelmaking operation, the time from the completion of the oxidization at the end of the oxidation to the tapping is usually referred to as the reduction period. Its main task is to make reducing slag for diffusion, deoxidation, desulfurization, control of chemical composition and temperature adjustment. At present, the high-power and ultra-power electric arc furnace steelmaking operations have canceled the reduction period.
Secondary Refining: The steelmaking process in which the molten steel in the steelmaking furnace (converter, electric furnace, etc.) is transferred to another vessel for refining, also called secondary metallurgy. The steelmaking process is therefore divided into two steps: initial refining and refining. Primary refining: The charge is melted, dephosphorized, decarburized and main alloyed in an oxidizing atmosphere furnace. Refining: Degassing, deoxidizing, desulfurizing, removing inclusions and fine-tuning components in a vacuum, inert gas or reducing atmosphere vessel. The benefits of splitting steel into two steps are improved steel quality, shorter smelting time, simplified process and lower production costs. There are many kinds of secondary refining, which can be roughly divided into two types: refining under normal pressure and refining under vacuum. According to different treatment methods, it can be divided into ladle processing type secondary refining and ladle refining type secondary refining.
Stirring of Molten Steel: Stirring of molten steel during refining outside the furnace. It homogenizes the molten steel composition and temperature and promotes metallurgical reactions. Most metallurgical reaction processes are phase-interfacial reactions, and the rate of diffusion of reactants and products is a limiting step in these reactions. When the molten steel is at rest, the metallurgical reaction speed is very slow. For example, the desulfurization of the molten steel in the electric furnace takes 30 to 60 minutes. In the refining, it takes only 3 to 5 minutes to desulfurize by stirring the molten steel. When the molten steel is in a static state, the inclusions are floated and removed, and the removal speed is slow; when the molten steel is stirred, the removal rate of the inclusions increases exponentially and is related to the stirring strength, the type and the characteristics and concentration of the inclusions.
Ladle Feeding, ladle processing, ladle refining, inert gas treatment, composition control, silicon enhancement, endpoint control.
Steel Tapping: The operation of discharging molten steel when the temperature and composition of the molten steel reach the specified requirements of the steel grade.
Precautions
Care should be taken to prevent slag from flowing into the ladle when tapping. Additives for adjusting the temperature, composition, and deoxidation of molten steel are added to the ladle or tapping stream during the tapping process, also called deoxidation alloying.
More News You May Interesting:
The Development Trends and Advantages of Electric Arc Furnaces
The Advantage and Disadvantage of Electric Arc Furnace and Induction Furnace
The Advantage of Induction Furnace (Medium Frequency Furnace)
Continuous Casting Machine Equipment







.jpg)








没有评论:
发表评论